A new study published in the journal Nature on Monday shows an association between brain size and structure among those infected by the Covid-19 virus.
The study, led by the Wellcome Centre for Integrative Neuroimaging at the University of Oxford, found “strong evidence for brain-related abnormalities” in COVID-19 patients who had had their brains scanned prior to their infection and then after they were either hospitalized with the virus or diagnosed as positive.
Comparing images of brains taken before and after infection, according to the study’s abstract:
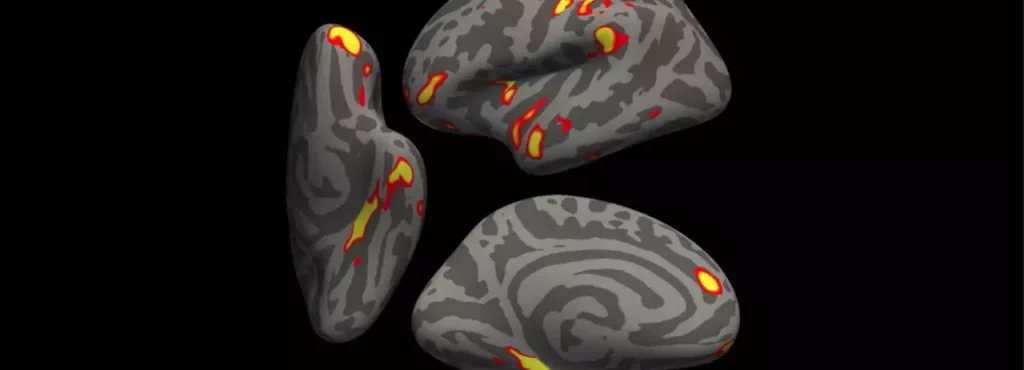
We identified significant longitudinal effects when comparing the two groups, including: (i) greater reduction in grey matter thickness and tissue-contrast in the orbitofrontal cortex and parahippocampal gyrus, (ii) greater changes in markers of tissue damage in regions functionally-connected to the primary olfactory cortex, and (iii) greater reduction in global brain size.
Researchers also say the study revealed a cognitive decline in patients, even those who did not become sick enough to need hospitalization.
Professor Naomi Allen, the chief scientist at UK Biobank and a co-author of that study, said the study “is the only study in the world to be able to demonstrate ‘before vs after’ changes in the brain associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Collecting the second set of multi-organ imaging scans from some people who had been infected with SARS-CoV-2 and from others who had not been infected has generated a unique resource to enable scientists to understand how the virus affects internal organs.”
According to the Guardian‘s reporting on the study:
Compared with 384 uninfected control subjects, those who tested positive for Covid had greater overall brain shrinkage and more grey matter shrinkage, particularly in areas linked to smell. For example, those who had Covid lost an additional 1.8% of the parahippocampal gyrus, a key region for smell, and an additional 0.8% of the cerebellum, compared with control subjects.
Disrupted signal processing in such areas may contribute to symptoms such as smell loss. Those who were infected also typically scored lower on a mental skills test than uninfected individuals. Lower scores were associated with a greater loss of brain tissue in the parts of the cerebellum involved in mental ability.
Dr Serena Spudich, who serves as chief of neurological infections and global neurology at the Yale School of Medicine but is not involved in the study, said the findings are striking.
“To me, this is pretty convincing evidence that something changes in brains of this overall group of people with Covid,” Spudich told the New York Times.
While potentially groundbreaking, the researchers involved said that more must be done to understand the long-term impacts of Covid-19 on the brain, including the impacts of more severe cases and the organ’s ability to heal after recovery from the virus.
Professor Gwenaëlle Douaud, lead author on the study, said she and her fellow researchers “were in a unique position to look at changes that took place in the brain following mild—as opposed to more moderate or severe—SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
“Despite the infection being mild for 96 per cent of our participants, we saw a greater loss of grey matter volume, and greater tissue damage in the infected participants, on average 4.5 months after infection,” Douaud added.
“They also showed greater decline in their mental abilities to perform complex tasks, and this mental worsening was partly related to these brain abnormalities. All these negative effects were more marked at older ages. A key question for future brain imaging studies is to see if this brain tissue damage resolves over the longer term.”
Republished from Commondreams.org



